how to calculate degrees of freedom
In case of equal dispersion of the data set the degree of freedom is calculated by this formula. Subtract 1 from the number of groups to find degrees of freedom between groups.
 |
| Degrees Of Freedom For Each Product Download Table |
So the freedom degrees of this data sample are 4.

. It is used in many contexts throughout statistics including hypothesis tests. The degrees of freedom is equal to the sum of the individual degrees of freedom for each sample. Calculate the degrees of freedom for the following samples assuming population variances are equal. On the packaging it reads.
The rule of thumb is that a. How To Compute Degrees of Freedom for Two Samples. D f N 1 Where as. Subtract the number of groups from.
Degrees of freedom refers to the maximum number of values that have the freedom to vary in a data sample. The free degree formula is equal to the size of a sample of data except one. Total freedom is the power or right to act speak or think without. The answer is no degree of freedom cannot be decimal.
The between treatment degrees of freedom is df1 k-1. D f Degrees of Freedom N Actual. Suppose if we have N number of gas molecules in the container then the total number of degrees of freedom is f 3N. Most of the time the restrictions are parametersthat are estimated as intermediate steps in calculating the statistic.
T x μ sn 300-310 18540 -34187. The degrees of freedom of a statistic is the sample size minus the number of restrictions. N1 352942982637578589 n2 5748037493830837 The first step is computing the. Next well calculate the degrees of freedom.
There are two types of freedom. The number of coefficients in your model is represented by the numerator or degrees of freedom minus the intercept. Df n -1 40 1 39. Since each sample has degrees of freedom equal to one less than their.
The general definition of degrees of freedom leads to the typical calculation of the total sample size minus the total number of. First well calculate the test statistic. As regards the vibrational motion two atoms oscillate against each other therefore both potential and kinetic energy the energy of vibration involve two degrees of freedom so that. Df N₁ N₂ 2 N₁ First sample entities N₂ Second sample entities Unequal Variances.
The number of degrees of freedom refers to the number of independent observations in a sample minus the number of population parameters that must be estimated from sample data. Calculating the degrees of freedom is often the sample size minus the number of parameters youre. The total degrees of freedom is N-1 and it is also true that k-1 N. To calculate degrees of freedom for ANOVA.
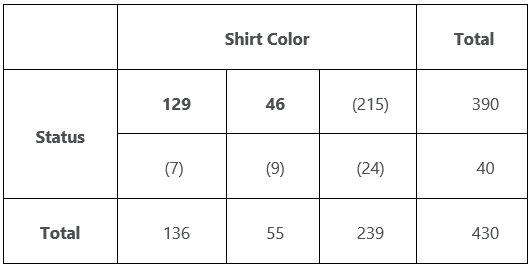
R is the number of restrictions usually the same as the number of paramete See more. Degrees of Freedom Formula The degrees of freedom formula is straightforward. The degrees of freedom in this case is r 1 c 1 where r is the number of rows number of different genes and c is the number of columns number of lists. Nis the sample size 1.
The error degrees of freedom is df2 N k. The degrees of freedom calculation we have done perfectly encapsulates this shrinkage to give us an estimate for the effective number of parameters we actually used. But if the system has q number of.
 |
| Degrees Of Freedom In Statistics Statistics By Jim |
 |
| Degrees Of Freedom What Are They Statistics How To |
 |
| Chi Squared Critical Values Degrees Of Freedom And Level Of Significance Youtube |
 |
| Degree Of Freedom In Statistics Meaning Examples Data Analytics |
 |
| Solved 3 1 1 2 3 Calculate The Mean Degrees Of Freedom Chegg Com |
Posting Komentar untuk "how to calculate degrees of freedom"